A Beginner’s Guide to Celiac Disease and Gluten-free Food

Extremely common yet deeply misunderstood and disregarded, celiac disease is one of the few disorders people don’t know enough about despite its wide prevalence in our populace.
Celiac disease isn’t as rare as it sounds, a chronic digestive and immune disorder triggered by eating foods containing gluten. More than 1 million celiac disease cases per year are reported in India, while 1 in every 133 Americans is found to have celiac disease.
Despite the staggering number of people inflicted by it, a lot of the world is oblivious to the symptoms of the ailment. Very little is known by the common people; thus, nothing about celiac disease comes into the limelight.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at every aspect of the disease and dive deeper into its intricacies.
What is celiac testing?
Many people experience symptoms even before they are diagnosed with the disease. Some telltale signs include diarrhea, bloating, wind, fatigue, anemia, and osteoporosis. Some people may also experience additional symptoms such as abdominal or joint pain and weight loss.
Getting tested in time to ascertain whether one has celiac disease is crucial. Blood or serologic tests are the most common means of checking for the disease. Some people might also have to undergo a biopsy of the small intestine for any signs of damage, as it is the most affected and vulnerable organ for patients with celiac disease.
What do you mean by gluten-free?
The ingestion of gluten is one of the primary causes of celiac disease. People with the ailment have an immune reaction to eating gluten which thus in turn, harms their small intestines. Avoiding foods that are devoid of gluten is the key to keeping your celiac disease in check and following a gluten-free lifestyle. Wheat, barley, rye, and oats are rich in gluten, as are some artificial colors and seasonings. Going off of these foods is what is meant by gluten-free.
What is gluten cross-contamination?
Gluten cross-contact or cross-contamination refers to the process where gluten-free food items become contaminated by either direct or indirect contact with gluten-rich products. This could happen unwittingly when you switch vessels that held wheat flour with gluten-free flour. Even the slightest physical touch between gluten and gluten-free products can put celiac at risk. One way to avoid this is by segregating gluten-free items in daily life from other gluten-rich products.
How to improve your symptoms?
One of the mainstays of curing or keeping celiac disease in check is going on a gluten-free diet. This is a precursor to any medicines you might take to relieve your aggravated symptoms. A gluten-free diet will not only promote intestinal healing but also reduce the symptoms tenfolds. Some doctors may also put patients on dietary supplements and vitamins to promote optimal health and even advise therapy and counseling to tackle issues such as depression and weight loss that come with the disease.
Are celiacs immunocompromised?
It is now widely considered that celiac disease patients are not immunocompromised, thus scrapping the notion that celiacs are at a greater risk of contracting viruses and infections such as covid. They are only averse to gluten which incites an immune reaction from the body, causing intestinal damage and other serious symptoms.
Long term complications
People who are untreated or don’t maintain a gluten-free diet must bear the brunt of the condition and celiac disease manifestation in the long term. They might experience malnutrition, bone weakening, infertility issues, lactose intolerance, nervous system problems, and sometimes cancer.
What if I accidentally consume gluten as a celiac?
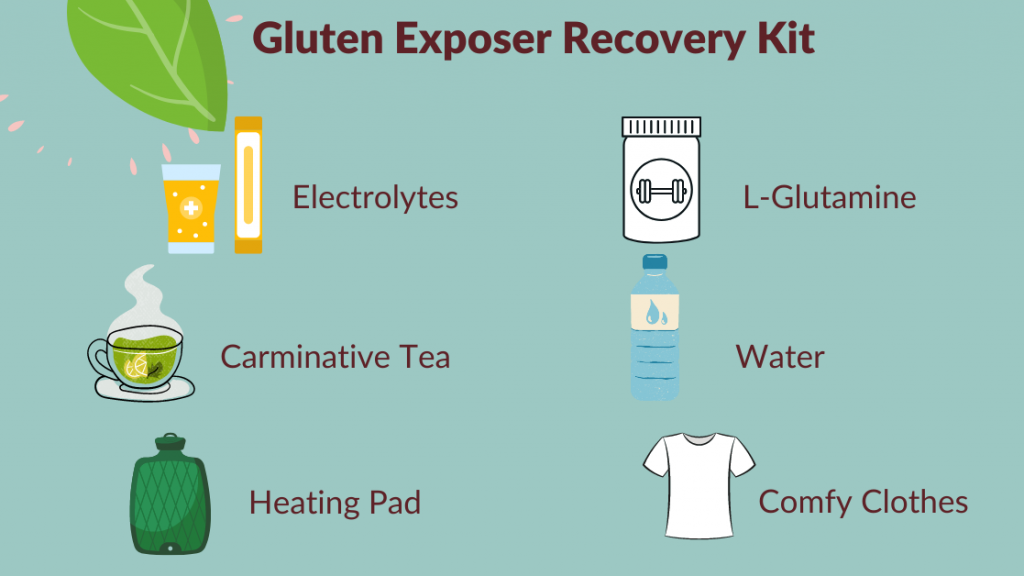
It happens to the best of us. With the market being flooded with products and food items, it’s difficult to pinpoint which one is gluten-free amidst the chaos. So if you accidentally end up ingesting gluten, your best course would be to take it easy and drink plenty of water. Consuming adequate water is vital to flushing out your system and relieving diarrhea. If you experience further malaise, speaking to your registered dietician or general practitioner would be advisable.
The life expectancy of people with celiac disease
Generally, people with the celiac disease under control have an average life expectancy. Problems crop up when patients do not adhere to a strict gluten-free diet leading to severe small intestinal damage in the long run and other long-term complications, as mentioned above.
Following up on your condition
Regular tests and screenings can help keep you in the loop on whether your celiac disease is in check. Many patients suffer from nutritional deficiencies despite going on a strict gluten-free diet. Following up without your doctor can help you gain adequate knowledge of these issues and tackle them with a clinical approach.
Final Thoughts
Celiac disease doesn’t have the level of mass awareness and societal recognition as other diseases despite its widespread prevalence. There’s a lot of stigmas attached to it, just like there once was with depression and other mental issues. Many still view celiac disease as a ‘rich people’s disease. This is due to the awareness of the disease in the upper classes of society. Nevertheless, regardless of social class, the disease is still found among the masses.
Many organizations and awareness camps are working towards normalizing the condition and helping spread awareness and information. Many organizations even go one step ahead by providing resources such as gluten-free foods and counseling sessions for celiac.
If you know someone who suffers from celiac disease, kindly do your part by spreading as much awareness as possible to bring this condition to light.
 MY JOURNEY
MY JOURNEY About Me
About Me Early life
Early life Diagnosis
Diagnosis CELIAC DISEASE
CELIAC DISEASE Symptoms & Diagnosis
Symptoms & Diagnosis Treatment & Follow Up
Treatment & Follow Up GLUTEN - FREE LIVING
GLUTEN - FREE LIVING At Home
At Home At School
At School At Social Events
At Social Events
 Grocery Shopping
Grocery Shopping COMMUNITY OUTREACH
COMMUNITY OUTREACH Gluten Free Meetup
Gluten Free Meetup Workshops
Workshops Webinars
Webinars COVID-19 Camps By Gluten Free Jio
COVID-19 Camps By Gluten Free Jio  Mid Day Meal
Mid Day Meal Beyond Celiac
Beyond Celiac Real Stories of Celiac
Real Stories of Celiac RESOURCES
RESOURCES Restaurant Dining Cards
Restaurant Dining Cards Recipes
Recipes Gluten Free eBook
Gluten Free eBook Gluten Free Jio App
Gluten Free Jio App RECOGNITION
RECOGNITION TRAVEL DIARY
TRAVEL DIARY



